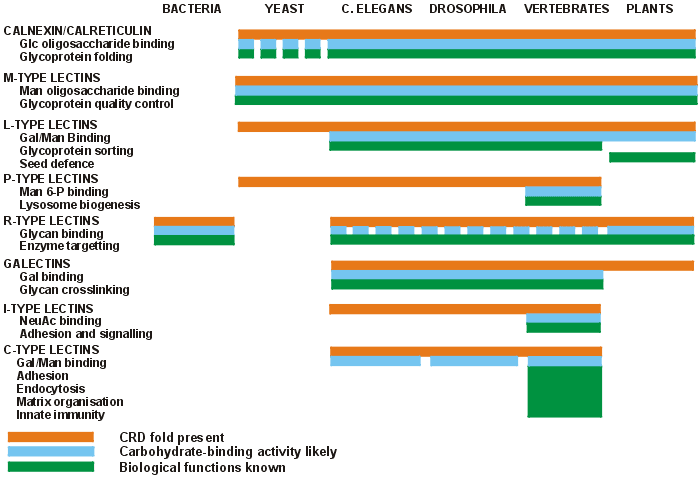
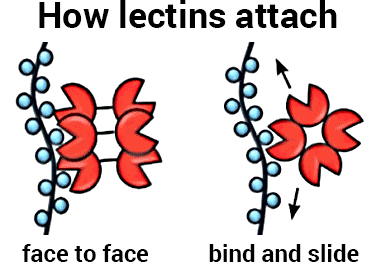
What are lectins?
“…Lectins are a defense mechanism which all life forms appear to have. Essentially, they are a low level toxin. The purpose of lectins is to discourage other animals from eating that life form. By triggering a negative reaction in the predator, that life form is then viewed as an undesirable food source. Hence, aiding its future survival1. …”
Seems like something we really ought to know more about, right?
“…Glyca-binding proteins (GBPs) are a category of proteins which bind specifically to certain sugar molecules. The “glyca” is the same prefix you see in the word glycation. That describes what happens after a protein or fat binds with a sugar molecule.
This binding process can cause inflammation and the creation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are compounds associated with numerous age-related diseases. It’s why the apparent anti-glycation benefits of carnosine are so intriguing1. …” https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carnosine
-
These 50 Foods Are High In Lectins: Avoidance or Not? https://www.superfoodly.com/foods-high-in-lectins/
-
L-carnosine: A Underutilized Dietary Supplement http://doctormurray.com/l-carnosine-a-underutilized-dietary-supplement/
-
Carnosine: A Possible Drug for Vascular Dementia metal chelator, anti-glycate, anti-neurodegenerative properties
https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/carnosine-a-possible-drug-for-vascular-dementia-2329-6925.1000146.php?aid=29082 -
Zinc, copper, and carnosine attenuate neurotoxicity of prion fragment PrP106-126. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/21442127/
-
Involvement of trace elements in the pathogenesis of prion diseases. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/25373386/
-
Neurotoxicity of Zinc: The Involvement of Calcium Homeostasis and Carnosine https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/brte/18/1/18_1_26/_pdf
-
Anti-Aggregating Effect of the Naturally Occurring Dipeptide Carnosine on Aβ1-42 Fibril Formation http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0068159
-
Carnosine inhibits ß-sheet formation of PrP106-126 and protects against its neurotoxicity http://aanddjournal.net/article/S1552-5260(09)00516-0/fulltext