Choline and Methionine (converts to choline in the body): Researchers believe it turns off the genes for visceral fat gain or storage…
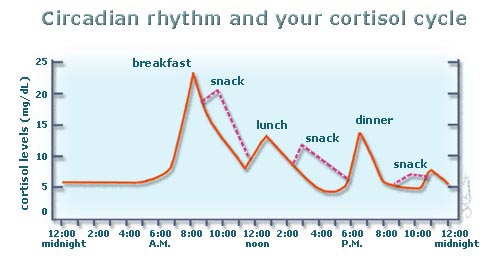
Another apparent reason; insulin resistance comes from spiking insulin too much or too many times throughout the day within a circadian cycle\rhythm (i.e. snacking in-between meals). After doing this for long periods of time day-in, day-out; insulin cell receptors shut down i.e. insulin resistance. (lots of physical activity involved where energy is needed changes the factors also but on the healthy metabolic side of the coin)
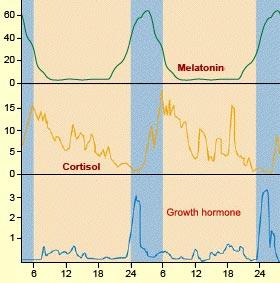
Keep in mind that snacking in-between meals in a resting metabolic state (no physical exertion being utilized) spikes cortisol (causing the visceral fat to populate on the internal organs; but choline blocks it) also, so when cortisol and insulin are being spiked they can block the fat burning hormones DHEA, Human Growth Hormone (HGH), and Testosterone (another fat burning hormone) which peak at the last stage of delta sleep and burn (oxidative break down i.e. ketones for energy) the fat throughout the day!
http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_11/i_11_p/i_11_p_hor/i_11_p_hor.html
QUOTE:
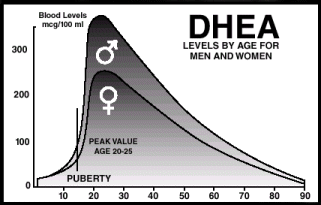
“…“Those readers who are considering following a ketogenic (low-carbohydrate) diet may be interested in a small study done on rheumatoid arthritis patients: the low-calorie ketogenic diet using less than 40 g of carbohydrates per day resulted in a 34% rise in DHEA within a week; the ketogenic diet was as effective as sub-total fast in raising DHEA levels. …”
http://www.lifeextension.com/magazine/2001/8/report_dhea/Page-01



