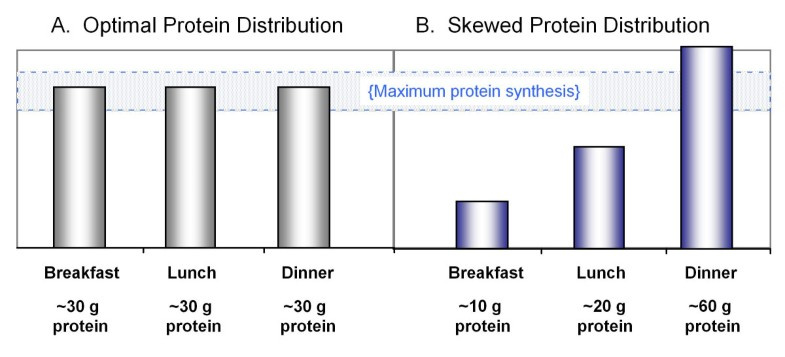
Maintaining and/or Increasing Muscle Mass
While there is good information on the amount of protein needed per day (grams per kilo of lean body mass), another vital factor is the amount of quality protein per meal/serving.
This has to do with…
mTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin)
It is a complex mechanism that that ensure muscle mass is maintained and/or increased.
mTOR is similar to a light switch. When the switch is on with mTOR, the lights are on; or in the case of mTOR, muscle mass is being maintained or increased.
When the mTOR “Light Switch” is off, the light aren’t on; or in the case of mTOR, muscle mass is not being maintained and preserved, let alone increased.
Protein mTOR Research
Research shows that a certain amount of quality protein is necessary for maintaining and increasing muscle mass.
The Dosage Per Meal/Serving
The amount of quality (dosage) per meal/serving is…
- Young Individuals: A minimum of 30 gram of quality protein per meal/serving.
These are individual approximately early 20’s or younger:
- Older Individuals: A minimum of 40 gram of quality protein per meal/serving.
These individual are approximately 30 years old, plus.
Quality Proteins
They are animal based: Meats, Cheeses, Eggs, etc.
Plant Protein are lower quality proteins.
The determinate factor of a protein being a good quality protein for turning on mTOR and maintaining or increasing muscle mass is the Amino Acid…
Leucine
As per the research…
-
Younger individual need approximately 2.5 gram per meal/serving.
-
Older individual need approximately 3.0 gram or more per meal/serving.
Doing The Math
Approximately 8% of quality proteins is composed of Leucine.
That means a younger individual would need approximately 30 gram per meal/serving; obtaining 2.4 gram of Leucine.
An older individual; individual would need approximately 40 gram per meal/serving; obtaining 3.2 gram of Leucine.
Reason For The Difference
Younger individual’s system are more efficient that older individuals.
The older individuals need more to elicit the same response.
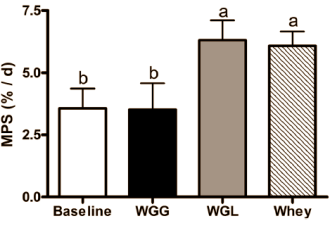
Supplementing Your Meal With Leucin
For individual who have a hard time consuming 40 gram of protein per meal/serving or individuals who are more into lower quality vegan proteins, supplementing a meal with Leucine Powder works.
This research demonstrated that…
Added leucine makes wheat protein as anabolic as whey
https://www.ergo-log.com/added-leucine-makes-wheat-protein-as-anabolic-as-whey.html
One more thing regarding Leucine.
Unflavored Leucine has an bitter, unpleasant taste. So, mixing it in something eliminates that issue.
Refractory Period
Optimal Muscle Protein Synthesis has to do with the length of time between meals/serving of protein.
Research show (Dr Layne Norton, Dr Gabe Wilson, and others) that Muscle Protein Synthesis is optimized when meals/serving are 4 - 6 hours apart.
The old Bodybuilding Protocol of consuming protein every three hours is counterproductive.
Sponge Example
Think of Muscle Protein Synthesis like a sponge.
A wet sponge is unable to soak up much, if any water.
However, if you allow the sponge to dry out completely, it absorb an enormous amount of water, compared to the wet sponge.
Metaphorically speaking, the same occurs with the time restriction for Muscle Protein Synthesis. You need to allow the “Muscle Protein Synthesis Sponge” to dry out.
Doing so, maximizes your Muscle Protein Synthesis.
More Information
Listed below is more in depth information on this…
Dr Donald Layman
THE TRUTH ABOUT PROTEIN: HOW MUCH AND HOW OFTEN?
https://simplyshredded.com/the-truth-about-protein.html
Kenny Croxdale