What does your blood glucose look like?
Does your blood ketone meter do blood glucose too?
“…You will likely have some blood ketones in your bloodstream when your blood glucose levels are low, but they may not be at the levels that many consider to be ‘optimal ketosis.’ As shown in the chart below, if your blood glucose levels are at 4.5mmol/L or 80 mg/dL then you you might expect blood ketone levels to be somewhere between 0.3 and 0.7mmol/L. If your blood sugars are as 4.9mmol/L or 88 mg/dL your ketones might be somewhere between 0.4 and 1.1 mmol/L. …”
0.4
“…While measuring ketones can be interesting, they tend to be a much noisier measurement. As the glucose in your blood reduced your body will be forced to turn to your body fat stores, so you will increase your fat burning. Part of the reason that you may not see high levels of ketones in your blood though is that they are being used efficiently for fuel and not backing up in your bloodstream. So if you have limited funds for test strips and don’t want to be pricking yourself too often then I would focus on blood glucose levels. …” …More
PERCENTILE (BHB %ile)? WHAT THE HECK IS THAT?
Crowdsourced ketone and glucose values:
”… In late 2015 I pooled a range of data from myself and a number of people on the Optimal Ketogenic Living (OKL) Facebook group. After sharing this data initially, a number of other people sent me their data. Later, Michel Lundell from Ketonix agreed to share an extensive set of anonymised data for me to analyse.
I hope that this crowd-sourced data will help to provide more clarity about optimal ketone levels in a similar way to Dr Bernstein surveying the glucose metre sales reps helped to provide a better understanding of what normal ketone values are.
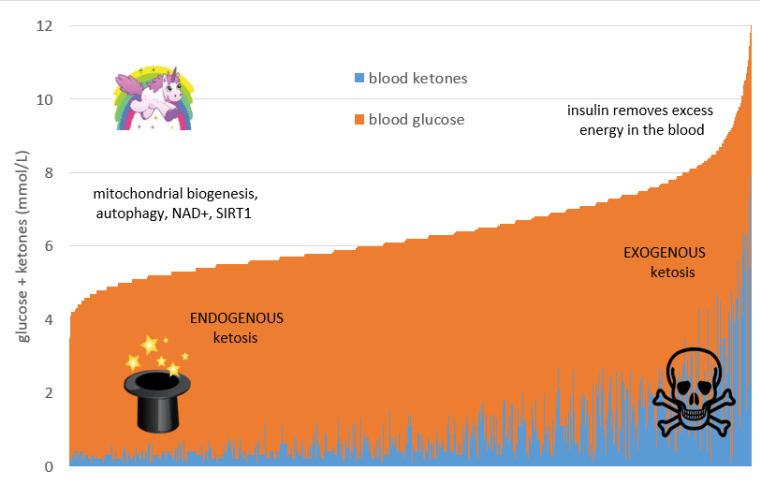
The chart below shows the sum of the blood glucose and ketones (i.e. total energy) from nearly three thousand data points from a broad range of people following a low carb or ketogenic dietary approach.
On the right-hand side of the chart, we have a high energy situation from both glucose and ketones. While not as extreme, high energy situation is similar to someone with Type 1 diabetes with high glucose and high ketone levels due to inadequate insulin. High levels of energy in the blood causes the pancreas to secrete insulin to hold the glycogen back in the liver and stop lipolysis (i.e. the release of fat from storage) until the energy in the bloodstream is used up.
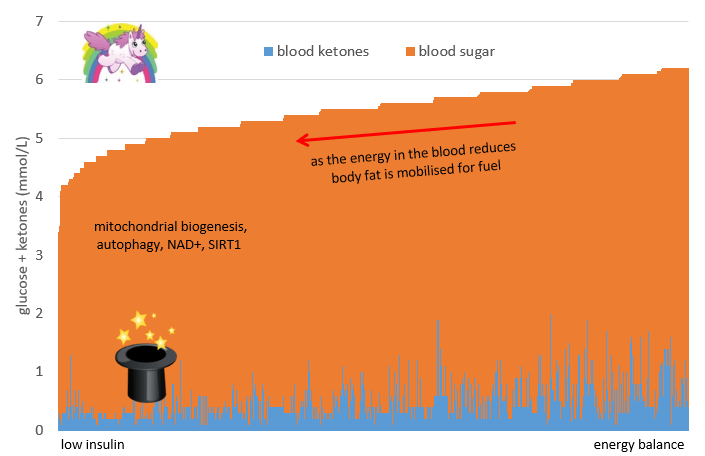
On the left-hand side of the chart, we have a low energy situation. These people do not have too much energy floating around in their bloodstream. They are also likely insulin sensitive and can easily access their body fat stores for fuel.
As shown in my fasting ketone data above, we may see high blood ketone levels when we go without food for an extended period. However, trying to replicate high ketone levels with high levels of exogenous ketones or an oversupply of dietary fat will not provide the same positive benefits as endogenous ketosis.
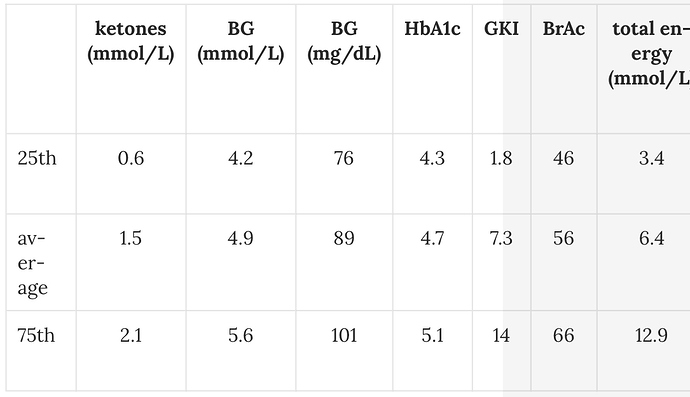
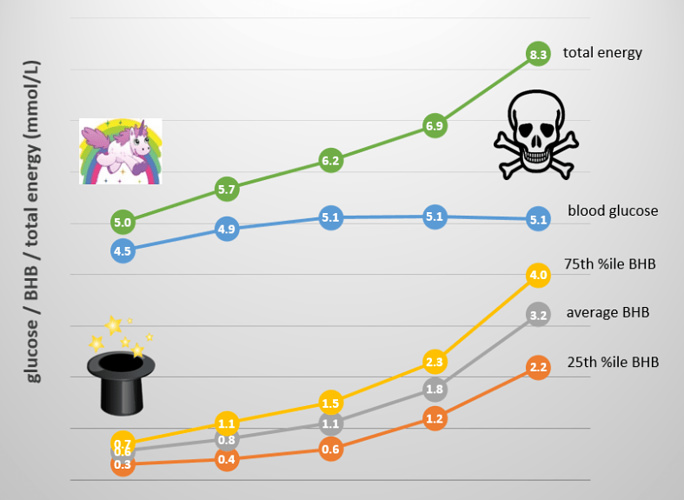
Based on this crowd-sourced data it seems the body tries to maintain a blood glucose level of around 4.9mmol/L and a blood ketone level (BHB) of around 1.5mmol/L. The table below shows this data in terms of average as well as the 25th percentile and 75th percentile points. …” …More