Some interesting things about Folic Acid and Folate:
[1] “…The majority of the pre-packaged. foods found in the grocery store have been through this process and fortified with folic acid. This is bad news for people with the MTHFR mutation. People with this mutation are unable to rid their bodies of folic acid. It builds up, blocking folate receptors and wrecking havoc. This build up is known as folic acid toxicity. Most lab tests do not distinguish between folic acid and folate when measuring blood levels. If folic acid intake is high, the results may show an individual has adequate amounts of folate. This is misleading as the individual actually has high levels of unusable folic acid, with little to no folate. This situation can cause the body to believe it is malnourished and result in unnecessary storing of energy (weight gain) bodies of folic acid. It builds up, blocking folate receptors and wrecking havoc. …More
[2] Folate-Related Polymorphisms:
Folate is found in dark green leafy vegetables like spinach and it serves two very important functions in the body. First, folate serves as a precursor to make new DNA. This is important for repairing a damed cell and for producing new cells whether we are talking about a sperm cell, or a brain cell (Figure 2). Second, folate serves as a precursor to make epigenetic factors, which change how much of a gene a given cell produces so that the gene does either more or less of a certain function. Epigenetics is discussed in more detail below.
There are a cluster of common polymorphisms in the folate metabolism pathway that affect the way the body metabolizes folate. These polymorphisms are in a gene known as MTHFR and can decrease its function between 40-90% (Figure 2). I have discussed MTHFR polymorphisms in a previous video. Supplementation with L-methylfolate along with other B vitamins has been shown to help overcome the MTHFR deficit . …”
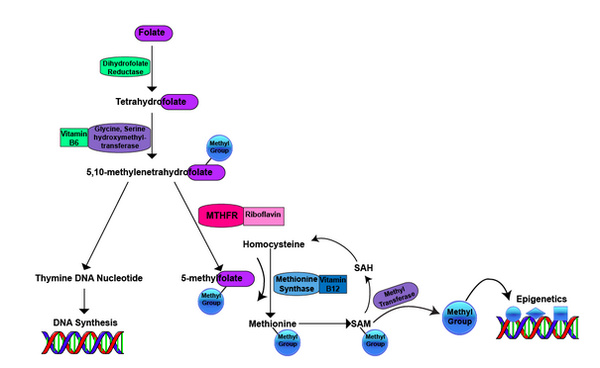
Figure 2: Folate Metabolism Pathway
Folate is converted into tetrahydrofolate, which is converted into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is required for two important pathways: 1). The synthesis of nucleic acids (thymine) required to make new DNA. 2). The production of 5-methylfolate by the riboflavin-dependent methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) enzyme. The methyl group from 5-methylfolate is used to convert homocysteine into the essential amino acid methionine (via methylation) by the vitamin B12-dependent methionine synthase enzyme. Methionine, is now methylated and is used as methyl donor via methyl transferase enzymes for a broad range of methylation reactions involved in epigenetics (DNA methylation). Once the methyl group is used from SAM, the methionine forms homocysteine again and the cycle starts over. * …More
[3] “…Beef liver is one of the most concentrated sources of folate available. A 3-ounce (85-gram) serving of cooked beef liver packs 212 mcg of folate, or about 54% of the RDI (30). In addition to folate, a single serving of beef liver can meet and exceed your daily requirements for vitamin A, vitamin B12 and copper (30). …” …More
[4] “…On the other hand, folic acid is a synthesized version of vitamin B9 that is added to processed foods and the common version used in supplements. Folic acid has a molecular structure that is nearly identical to folate. Due to their close resemblance, folic acid and folate are widely considered to be the same. …” …More


